



SMS Envoclean Private Limited.
Near Deonar Dumping Ground (W),
Opp.SatheNagar,Ghatkopar-Mankhurd link Road,Deonar, Mumbai-400043
Telephone numbers: 8879003572-7045686071 (/72/73/74)
Toll Free Number – 1800 2666 575
Email id: [email protected]


SMS WATER GRACE BMW PVT. LTD.
DJB Sewage Treatment Plant
Nilothi Village
New Delhi -110041
Ph. No. 8744076006 / 32 / 34 /01


SMS-Watergrace Enviroprotect Pvt. Ltd
Khasra No 70/1, 70/2, & 70/5,
Phase No. 2, Near Drolia Plant, Village Siltara, RNM Dharsiwa,Dist. Raipur, Pincode-493111
Customer Care-+918871758422
Email [email protected]


Kailas Plant
Kailas Crematorium Compound, Next to Naidu Hospital, Pune – 411001


Moshi Plant
Gat.No.458,460,461, Moshi Kachara Depo, Pune Nashik Highway,Moshi Tal- Haveli Dist – Pune


SMS Envoclean Private Limited.
Near Deonar Dumping Ground (W),
Opp.SatheNagar,Ghatkopar-Mankhurd link Road,Deonar, Mumbai-400043
Telephone numbers: 8879003572-7045686071 (/72/73/74)
Toll Free Number – 1800 2666 575
Email id: [email protected]


SMS WATER GRACE BMW PVT. LTD.
DJB Sewage Treatment Plant
Nilothi Village
New Delhi -110041
Ph. No. 8744076006 / 32 / 34 /01


SMS-Watergrace Enviroprotect Pvt. Ltd
Khasra No 70/1, 70/2, & 70/5,
Phase No. 2, Near Drolia Plant, Village Siltara, RNM Dharsiwa,Dist. Raipur, Pincode-493111
Customer Care-+918871758422
Email [email protected]


SMS Watergrace Mediwaste Management Private Limited.
313 KHA, Gram-Bindowa,
Tehsil Mohanlalganj,
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
TelePhone No. – 8172811601,8172811603, 8172811604Email id – [email protected] , [email protected]


Kailas Plant
Kailas Crematorium Compound, Next to Naidu Hospital, Pune – 411001


Moshi Plant
Gat.No.458,460,461, Moshi Kachara Depo, Pune Nashik Highway,Moshi Tal- Haveli Dist – Pune
























SMS Envoclean Private Limited.
Near Deonar Dumping Ground (W),
Opp. Sathe Nagar,
Ghatkopar-Mankhurd link Road,
Deonar, Mumbai-400043
Telephone numbers: 8879003572-7045686071 (/72/73/74)
Toll Free Number – 1800 2666 575
Email id: [email protected]


SMS WATERGRACE BMW PVT. LTD.
DJB Sewage Treatment Plant
Nilothi Village
New Delhi -110041
Ph. No. 8744076006 / 32 / 34 /01


SMS-Watergrace Enviroprotect Pvt. Ltd
Khasra No 70/1, 70/2, & 70/5,
Phase No. 2, Near Drolia Plant, Village Siltara, RNM Dharsiwa,Dist. Raipur, Pincode-493111
Customer Care-+918871758422
Email [email protected]


SMS Watergrace Mediwaste Management Private Limited.
313 KHA, Gram-Bindowa,
Tehsil Mohanlalganj,
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
TelePhone No. – 8172811601,8172811603, 8172811604 Email id [email protected] ,[email protected]


Kailas Plant
Kailas Crematorium Compound, Next to Naidu Hospital, Pune – 411001


Moshi Plant
Gat.No.458,460,461, Moshi Kachara Depo, Pune Nashik Highway,Moshi Tal- Haveli Dist – Pune


SMS Envoclean Private Limited.
Near Deonar Dumping Ground (W),
Opp. Sathe Nagar,
Ghatkopar-Mankhurd link Road,
Deonar, Mumbai-400043
Telephone numbers: 8879003572-7045686071 (/72/73/74)
Toll Free Number – 1800 2666 575
Email id: [email protected]


SMS WATER GRACE BMW PVT. LTD.
DJB Sewage Treatment Plant
Nilothi Village
New Delhi -110041
Ph. No. 8744076006 / 32 / 34 /01


SMS-Watergrace Enviroprotect Pvt. Ltd
Khasra No 70/1, 70/2, & 70/5,
Phase No. 2, Near Drolia Plant, Village Siltara, RNM Dharsiwa,Dist. Raipur, Pincode-493111
Customer Care-+918871758422
Email [email protected]


SMS Watergrace Mediwaste Management Private Limited.
313 KHA, Gram-Bindowa,
Tehsil Mohanlalganj,
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
TelePhone No. – 8172811601,8172811603, 8172811604 Email id [email protected] ,[email protected]


Kailas Plant
Kailas Crematorium Compound, Next to Naidu Hospital, Pune – 411001


Moshi Plant
Gat.No.458,460,461, Moshi Kachara Depo, Pune Nashik Highway,Moshi Tal- Haveli Dist – Pune


















(a) Human Anatomical Waste: Human tissues,organs body parts and fetus below the viability period (as per the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 1971, amended from time to time).

Yellow coloured non-chlorinated plastic bags

(b) Animal Anatomical Waste : Experimental animal carcasses, body parts, organs, tissues, including the waste generated from animals used in experiments or testing in veterinary hospitals or colleges or animal houses.

(c) Soiled Waste:
Items contaminated with
blood, body fluids like
dressings, plaster casts,
cotton swabs and bags
containing residual or
discarded blood and
blood components.

Yellow coloured non-chlorinated plastic bags
Incineration or Plasma
Pyrolysis or
deep burial
In absence of above
facilities, autoclaving or
micro-waving/
hydroclaving followed by
shredding or mutilation
or combination of
sterilization and
shredding. Treated
waste to be sent for
energy recovery.
(d) Expired or
Discarded Medicines:
Pharmaceutical waste
like antibiotics, cytotoxic
drugs including all items
contaminated with
cytotoxic drugs along
with glass or plastic
ampoules, vials etc.

Yellow coloured non chlorinated plastic bags or
containers
Expired `cytotoxic drugs
and items contaminated
with cytotoxic drugs to
be
returned back to the
manufacturer or supplier
for incineration at
temperature >1200 deg
C or to common bio-
medical waste treatment
facility or hazardous
waste treatment,
storage and disposal
facility for incineration at
>1200 deg C Or
Encapsulation or
Plasma Pyrolysis at
>1200 deg C.
All other discarded
medicines shall be
either sent back to
manufacturer or
disposed by incineration.
(e) Chemical Waste:
Chemicals used in production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants.

Yellow coloured containers or
non-chlorinated plastic bags
Disposed of by
incineration or Plasma
Pyrolysis or
Encapsulation in
hazardous waste
treatment, storage and
disposal facility.
(f) Chemical Liquid
Waste :
Liquid waste generated
due to use of chemicals
in production of biological
and used or discarded
disinfectants, Silver X-ray
film developing liquid,
discarded Formalin,
infected secretions,
aspirated body
fluids, liquid from
laboratories and floor
washings, cleaning,
house-keeping and
disinfecting activities etc.

Separate collection system leading to effluent treatment system
After resource recovery,
the chemical liquid
waste shall be pre-
treated before mixing
with other wastewater.
The combined discharge
shall conform to the
discharge norms given
in Schedule-
III.
(g) Discarded linen,
mattresses, beddings
contaminated with blood
or body fluid.
Non-chlorinated
yellow plastic bags or suitable packing material
Non- chlorinated chemical disinfection
followed by incineration or Plazma Pyrolysis or for energy recovery In absence of above facilities, shredding or mutilation or combination of sterilization and shredding. Treated waste to be sent for energy recovery or incineration or Plazma Pyrolysis.
(h) Microbiology,
Biotechnology and other
clinical laboratory waste:
Blood bags, Laboratory
cultures, stocks or
specimens of
microorganisms, live or
attenuated vaccines,
human and animal cell
cultures used in
research, industrial
laboratories, production
of biological, residual
toxins, dishes and
devices used for cultures.

Autoclave safe plastic bags or containers
Autoclave safe plastic bags or containers
(a) Human Anatomical Waste: Human tissues,organs body parts and fetus below the viability period (as per the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 1971, amended from time to time).

(b) Animal Anatomical Waste : Experimental animal carcasses, body parts, organs, tissues, including the waste generated from animals used in experiments or testing in veterinary hospitals or colleges or animal houses.

(c) Soiled Waste:
Items contaminated with
blood, body fluids like
dressings, plaster casts,
cotton swabs and bags
containing residual or
discarded blood and
blood components.

(d) Expired or
Discarded Medicines:
Pharmaceutical waste
like antibiotics, cytotoxic
drugs including all items
contaminated with
cytotoxic drugs along
with glass or plastic
ampoules, vials etc.

(e) Chemical Waste:
Chemicals used in production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants.

(f) Chemical Liquid
Waste :
Liquid waste generated
due to use of chemicals
in production of biological
and used or discarded
disinfectants, Silver X-ray
film developing liquid,
discarded Formalin,
infected secretions,
aspirated body
fluids, liquid from
laboratories and floor
washings, cleaning,
house-keeping and
disinfecting activities etc.

(g) Discarded linen,
mattresses, beddings
contaminated with blood
or body fluid.

(h) Microbiology,
Biotechnology and other
clinical laboratory waste:
Blood bags, Laboratory
cultures, stocks or
specimens of
microorganisms, live or
attenuated vaccines,
human and animal cell
cultures used in
research, industrial
laboratories, production
of biological, residual
toxins, dishes and
devices used for cultures.

Yellow coloured non chlorinated plastic bags or
containers
Yellow coloured containers or
non-chlorinated plastic bags
Separate collection system leading to effluent treatment system
Non-chlorinated
yellow plastic bags or suitable packing material
Autoclave safe plastic bags or containers
Incineration or Plasma
Pyrolysis or
deep burial
In absence of above
facilities, autoclaving or
micro-waving/
hydroclaving followed by
shredding or mutilation
or combination of
sterilization and
shredding. Treated
waste to be sent for
energy recovery.
Expired `cytotoxic drugs
and items contaminated
with cytotoxic drugs to
be
returned back to the
manufacturer or supplier
for incineration at
temperature >1200 deg
C or to common bio-
medical waste treatment
facility or hazardous
waste treatment,
storage and disposal
facility for incineration at
>1200 deg C Or
Encapsulation or
Plasma Pyrolysis at
>1200 deg C.
All other discarded
medicines shall be
either sent back to
manufacturer or
disposed by incineration.
Disposed of by
incineration or Plasma
Pyrolysis or
Encapsulation in
hazardous waste
treatment, storage and
disposal facility.
After resource recovery,
the chemical liquid
waste shall be pre-
treated before mixing
with other wastewater.
The combined discharge
shall conform to the
discharge norms given
in Schedule-
III.
Non- chlorinated chemical disinfection
followed by incineration or Plazma Pyrolysis or for energy recovery.
In absence of above facilities, shredding or mutilation or combination of sterilization and shredding. Treated waste to be sent for energy recovery or incineration or Plazma Pyrolysis.
Pre-treat to sterilize with non-chlorinated
chemicals on-site as per National AIDS Control Organisation or
World Health Organisation guidelines
thereafter for Incineration.
Non-chlorinated
yellow plastic bags or suitable packing material
Autoclave safe plastic bags or containers










Contaminated Waste
(Recyclable)
(a) Wastes generated from disposable items such as tubing, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, syringes (without
needles and fixed needle syringes) and vaccutainers with their needles cut) and gloves.


Waste sharps
including Metals:
Needles, syringes with fixed needles, needles from needle tip cutter or burner, scalpels, blades, or any other contaminated sharp object that may cause puncture and cuts. This includes both used,
discarded and contaminated metal sharps



Contaminated Waste
(Recyclable)
(a) Wastes generated from disposable items such as tubing, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, syringes (without
needles and fixed needle syringes) and vaccutainers with their needles cut) and gloves.
Cardboard boxes
with blue colored marking

Disinfection (by soaking the washed
glass waste after cleaning with
detergent and Sodium Hypochlorite treatment) or through autoclaving or
microwaving or hydroclaving and then
sent for recycling.
(b) Metallic Body
Implants
Cardboard boxes with blue
colored marking
Cardboard boxes with blue
colored marking
Contaminated Waste
(Recyclable)
(a) Wastes generated from disposable items such as tubing, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, syringes (without
needles and fixed needle syringes) and vaccutainers with their needles cut) and gloves.
(b) Metallic Body
Implants
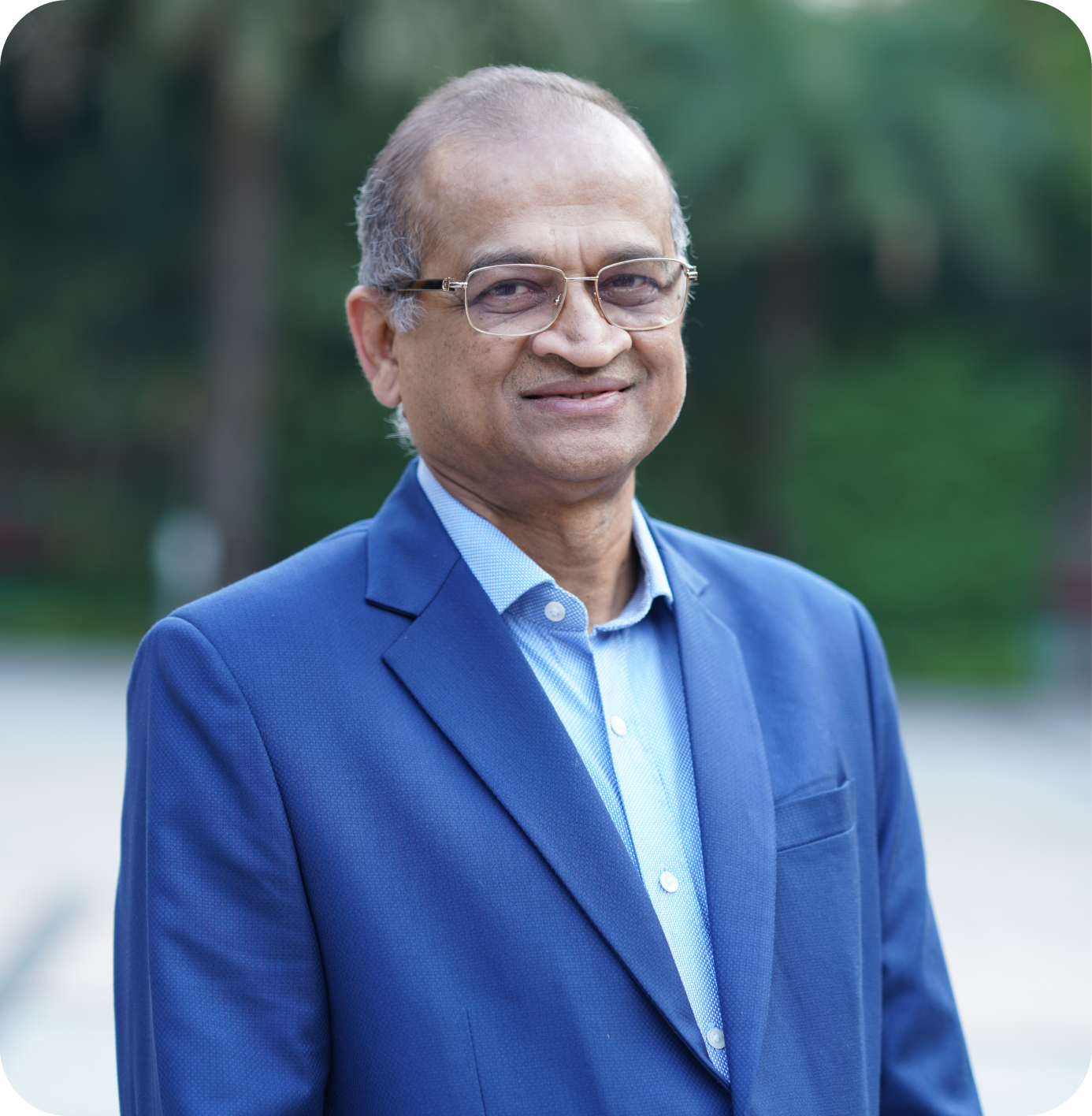




He is a Chartered Accountant and having experience of working in industrial environment since 1980. He has traveled extensively around the globe and worked in India, Indonesia and Sri Lanka.Born in Jodhpur, India on 12th June 1956. Did his graduation (1976-79) from GCA, Ajmer and CA (1980) from Mumbai. He started career from Kalpataru, Mumbai, later shifted to Nagpur and worked for FACOR, Star Circlips and Coventry Springs till 1990. In 1990 he joined INDORAMA and got shifted to Indonesia. In 2001 after working for a brief period in Thailand and Sri Lanka returned India & decided to settle in Nagpur and after doing few ventures joined SMS Group to setup an Environment & Clean Energy Division.